What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are a common health concern that can affect people of various ages. This condition involves the swelling of blood vessels in the rectal and anal area, leading to discomfort and pain. Understanding hemorrhoids is essential for adopting effective management strategies and finding relief from the associated symptoms.
One of the key characteristics of hemorrhoids is the enlargement of blood vessels around the anus, which can cause itching, pain, and bleeding. Exploring information about hemorrhoids can guide individuals in making informed decisions about their health and seeking appropriate care when needed.
Hemorrhoids are very common in both men and women, with about half of all people experiencing hemorrhoids by age 50. Many women get hemorrhoids during pregnancy and childbirth due to the extra stress on blood vessels in the pelvic area caused by carrying a baby in the belly. Additionally, straining during childbirth can further increase pressure on these blood vessels.
For those looking for ways to manage hemorrhoids and alleviate their discomfort, consulting healthcare professionals with expertise in this area is crucial. With the right guidance and personalized treatment plans, individuals can find relief and enhance their overall well-being.
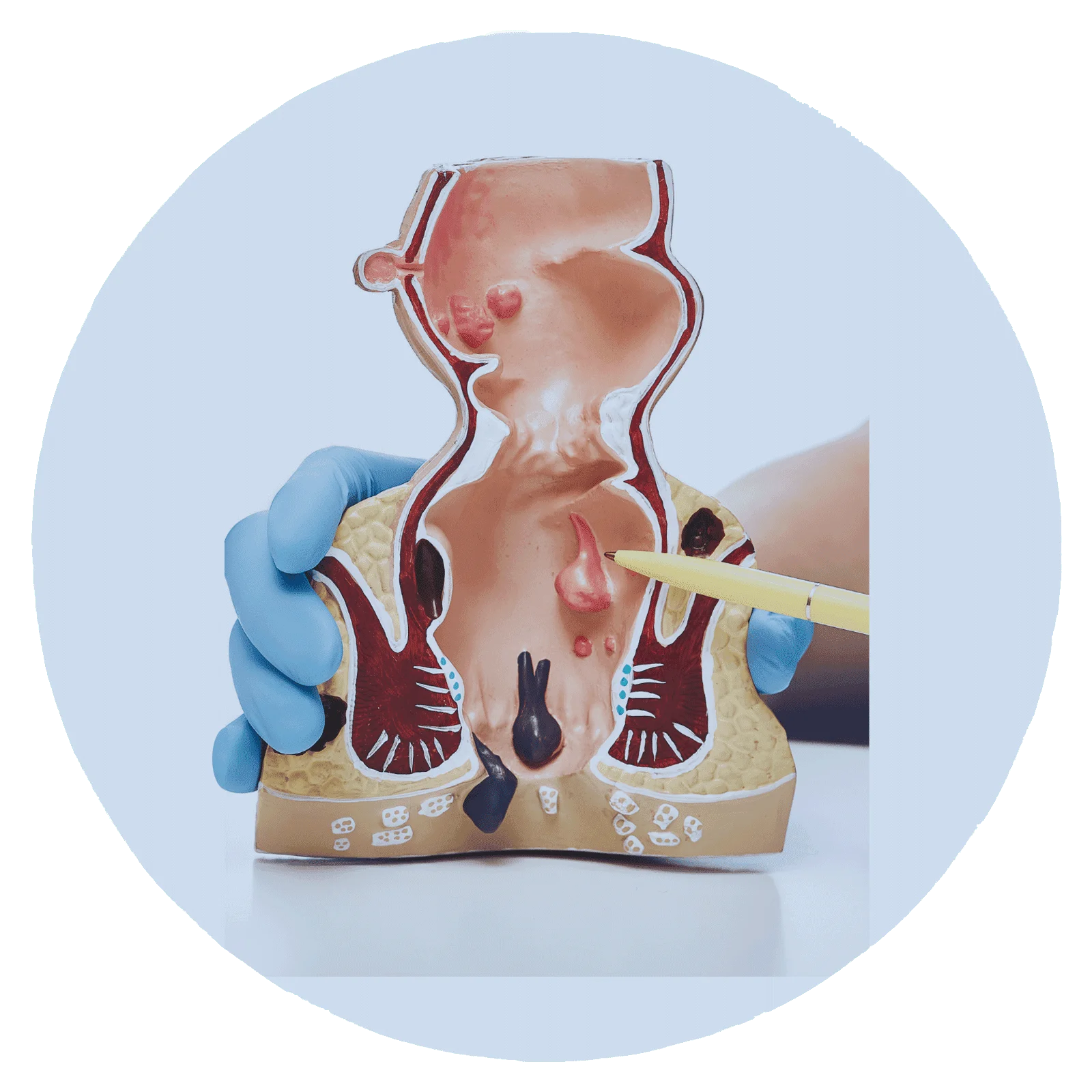
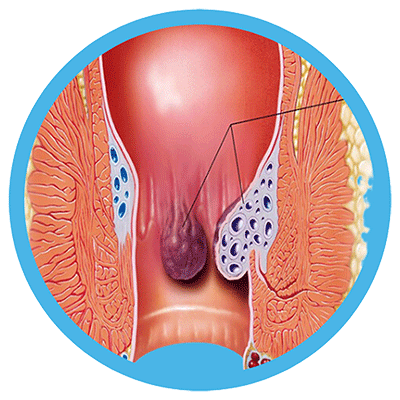
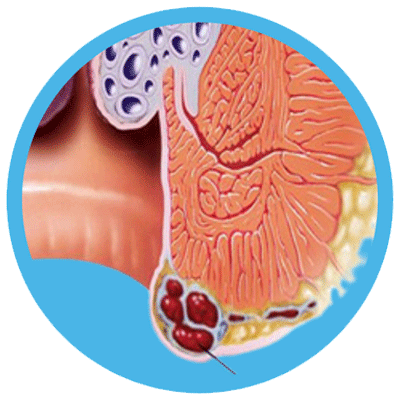
Types of Hemorrhoids
1- Internal Hemorrhoids:
- These are located inside the rectum and are generally painless, as they are above the anal sphincter.
- Symptoms may include bleeding during bowel movements. Blood may be visible on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
2- External Hemorrhoids:
- These are located under the skin around the anus and can be felt as small, tender lumps.
- Symptoms may include itching, pain, and swelling around the anal area.
Different Stages of Hemmorrhoids
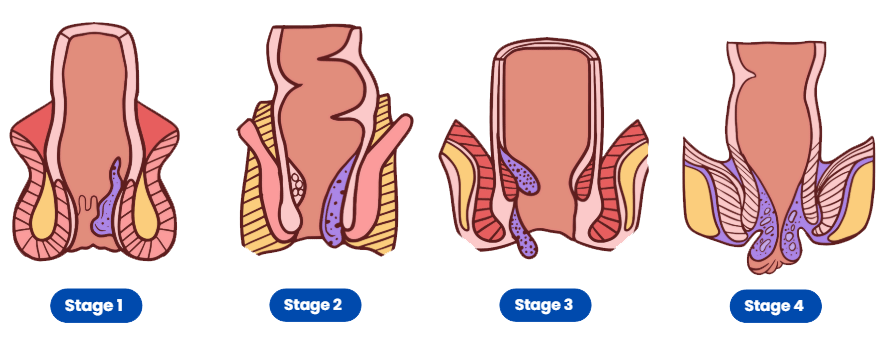
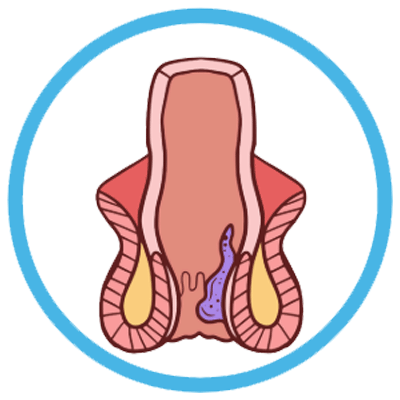
Stage 1 (First-Degree Hemorrhoids):
- Stage 1 hemorrhoids are the mildest form and often do not protrude from the anus.
- They may cause minimal or no symptoms.
- Symptoms, if present, may include mild itching or discomfort.
Stage 2 (Second-Degree Hemorrhoids):
- Stage 2 hemorrhoids prolapse (extend) outside the anus during bowel movements but retract (go back inside) spontaneously afterward.
- They may cause more noticeable symptoms such as pain, itching, and discomfort.
- Bleeding during bowel movements may also occur.
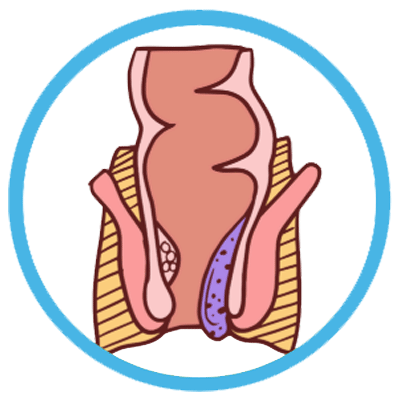
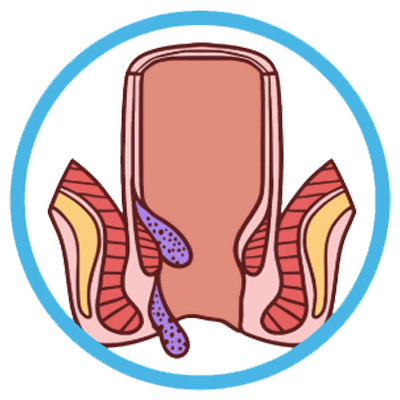
Stage 3 (Third-Degree Hemorrhoids):
- Stage 3 hemorrhoids prolapse outside the anus during bowel movements and require manual repositioning (pushing them back inside).
- Symptoms such as pain, itching, discomfort, and bleeding are often more pronounced.
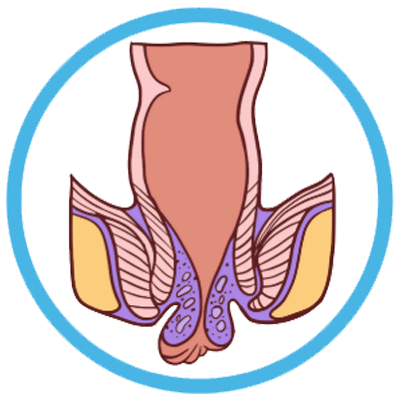
Stage 4 (Fourth-Degree Hemorrhoids):
- Stage 4 hemorrhoids are the most severe form and are characterized by permanent prolapse.
- They cannot be manually repositioned and may remain outside the anus all the time.
- Symptoms can be severe, including intense pain, bleeding, itching, and difficulty with hygiene.
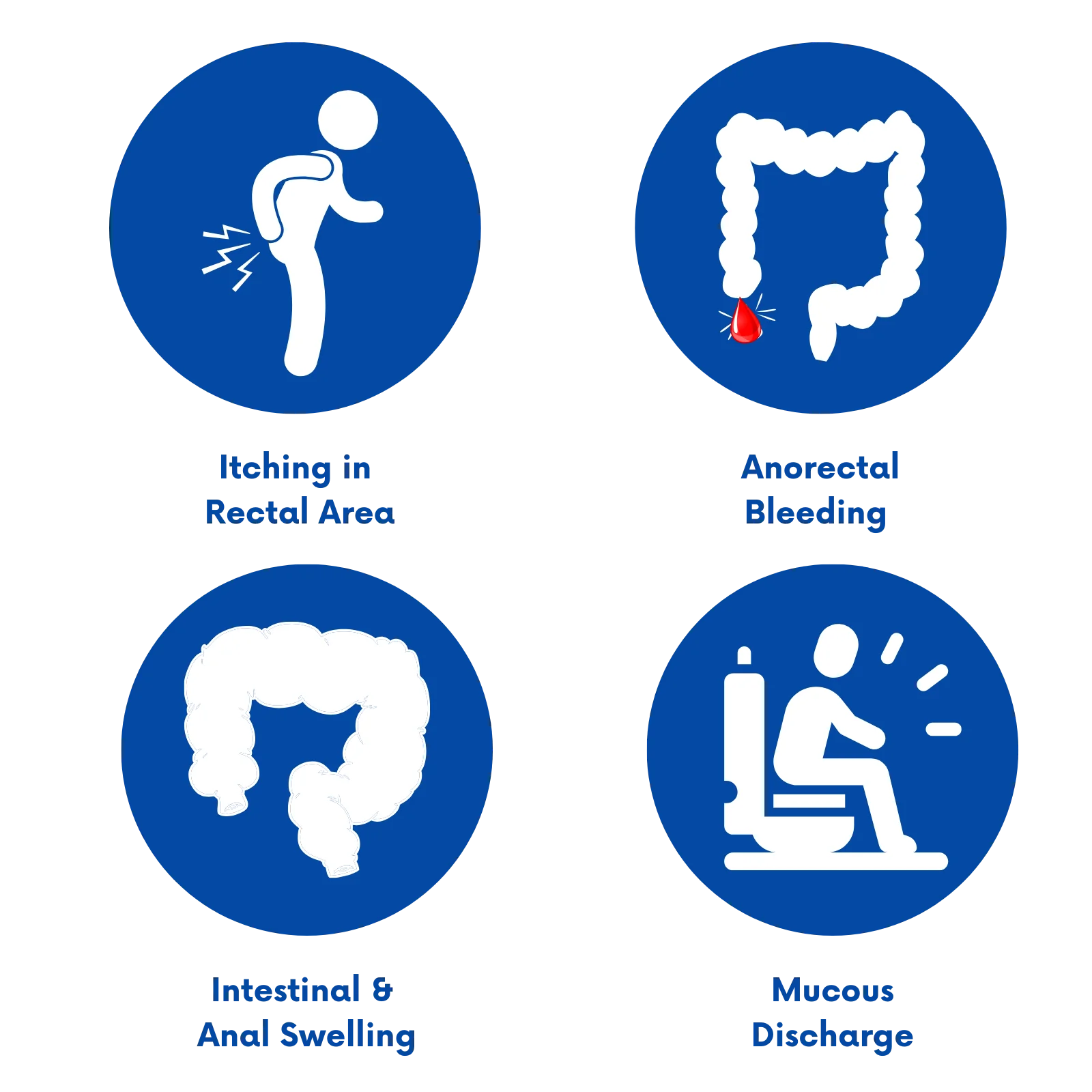
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can manifest with various symptoms, although they may vary from person to person. Common Hemorrhoids symptoms include discomfort, pain, or itching in the rectal area, as well as bleeding during bowel movements. Some individuals may also experience swelling or a lump near the anus, making sitting and passing stool uncomfortable.
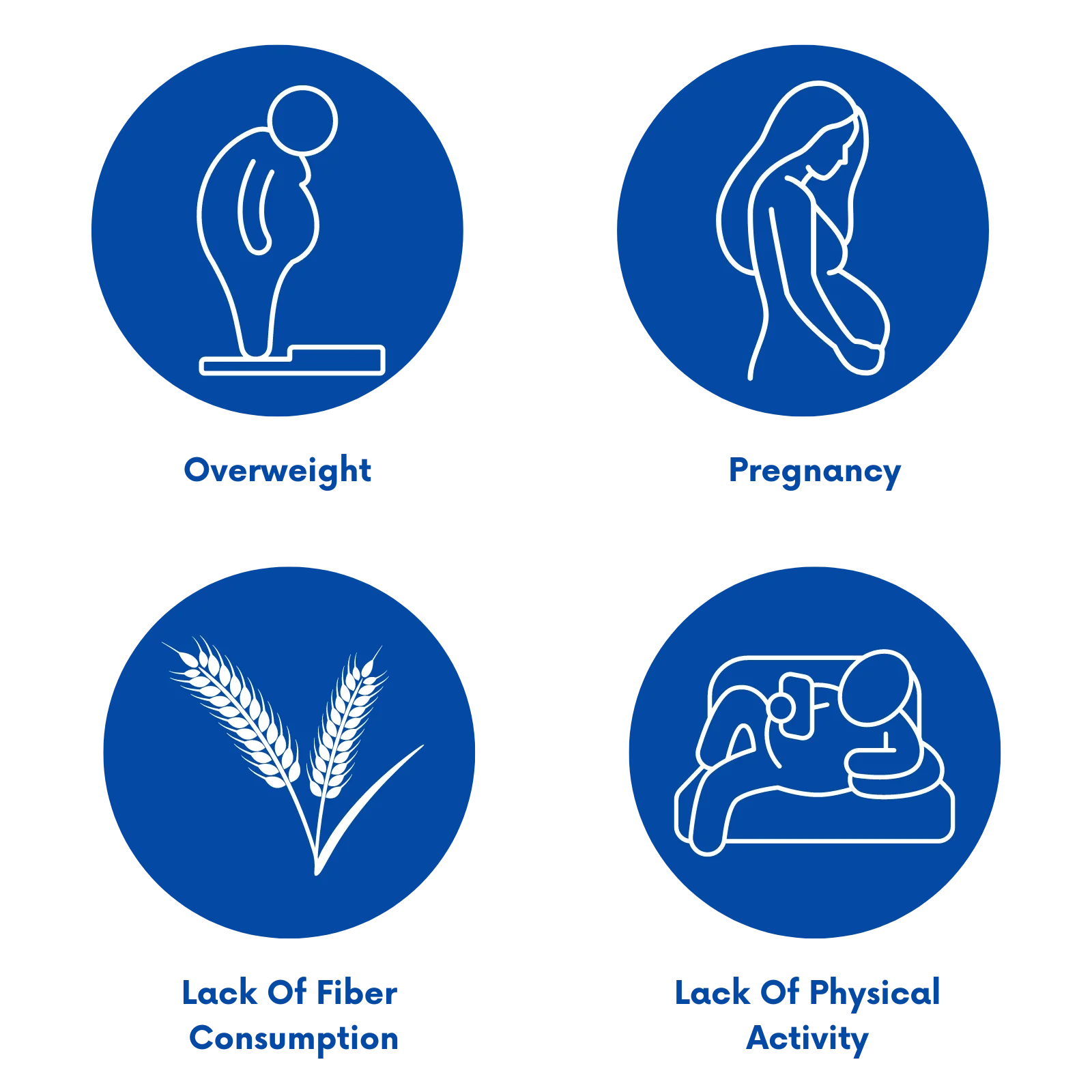
Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids
Various risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing hemorrhoids. These include being overweight or obese, leading a sedentary lifestyle, frequently lifting heavy objects, having chronic constipation or diarrhea, and being pregnant. Aging also plays a role, as the risk of hemorrhoids tends to increase with age.
Recognizing the symptoms and Understanding Hemorrhoids, along with the underlying causes and risk factors, is essential for adopting effective management strategies and seeking appropriate care. By addressing these contributing factors, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and enhance their overall well-being
Diagnosing Hemorrhoids
Diagnosing hemorrhoids typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and a physical examination by a healthcare professional, with a focus on Hemorrhoid Diagnosis.
This may include discussing symptoms such as discomfort, pain, bleeding, or itching in the anal area, as well as the presence of any lumps or swelling. A visual examination of the rectal area may be conducted to assess the condition.
Long-Term Health Risks
Hemorrhoids can be associated with certain long-term health risks and complications.
These might include chronic pain or discomfort, recurrent bleeding, thrombosis (blood clot formation within the hemorrhoid), and prolapse (protrusion of hemorrhoid tissue from the anus). While hemorrhoids are generally not life-threatening, seeking proper medical guidance and adopting preventive measures can help manage these potential risks effectively.
Managing Hemorrhoids
Effectively managing hemorrhoids involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, self-care measures, and medical interventions, all contributing to Hemorrhoid Management Strategies.

Healthy Eating
Adopting a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and maintaining regular bowel habits can help prevent constipation and reduce strain during bowel movements, which is a common trigger for hemorrhoids.

Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve circulation and prevent constipation, both of which contribute to hemorrhoid management.

Natural Remedies
Discover soothing relief with natural remedies. Consider incorporating these gentle approaches to support your journey in managing hemorrhoids effectively.

Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter creams, ointments, or suppositories can provide relief from itching, pain, and swelling associated with hemorrhoids. These products often contain ingredients like hydrocortisone or witch hazel.

Warm Baths
Soaking in warm water baths, also known as sitz baths, can help soothe the discomfort of hemorrhoids. This practice can improve blood flow and promote healing of the affected area.

Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to treat more severe or persistent hemorrhoids. These can include rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or minimally invasive surgery.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
if hemorrhoid symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to seek guidance from a healthcare provider for a deeper Understanding of Hemorrhoids. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment options based on the individual's condition.
By implementing these strategies and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can effectively deal with Hemorrhoids and make the pain and discomfort feel better.

